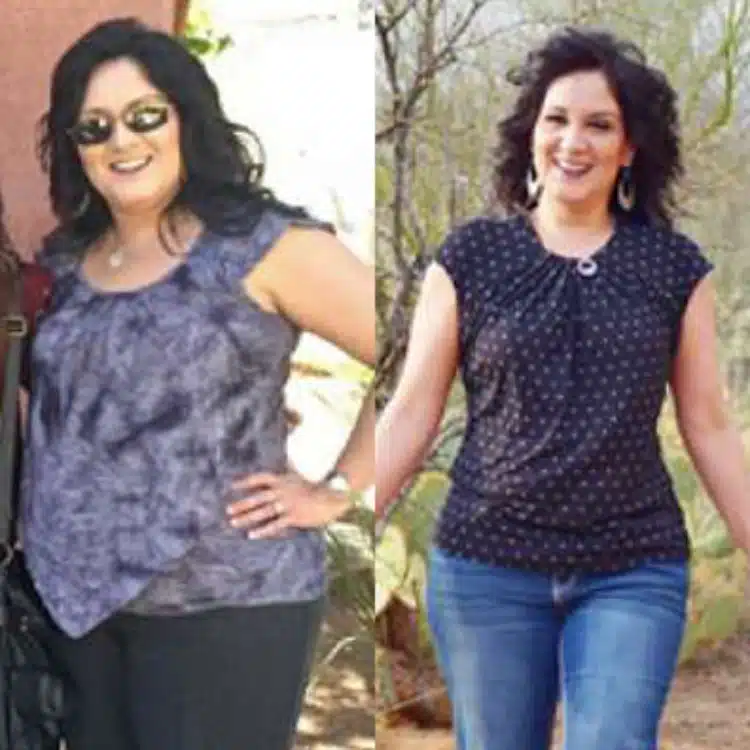
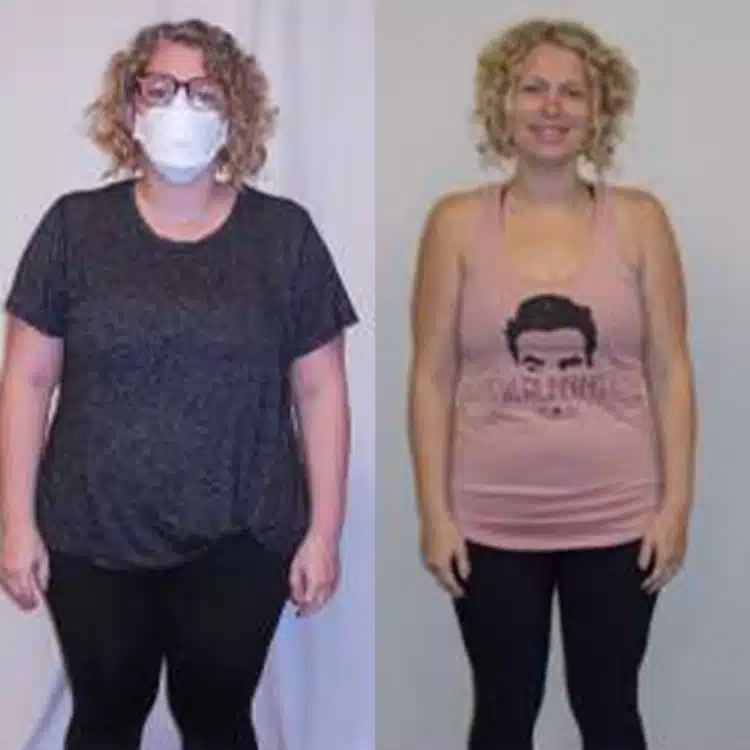
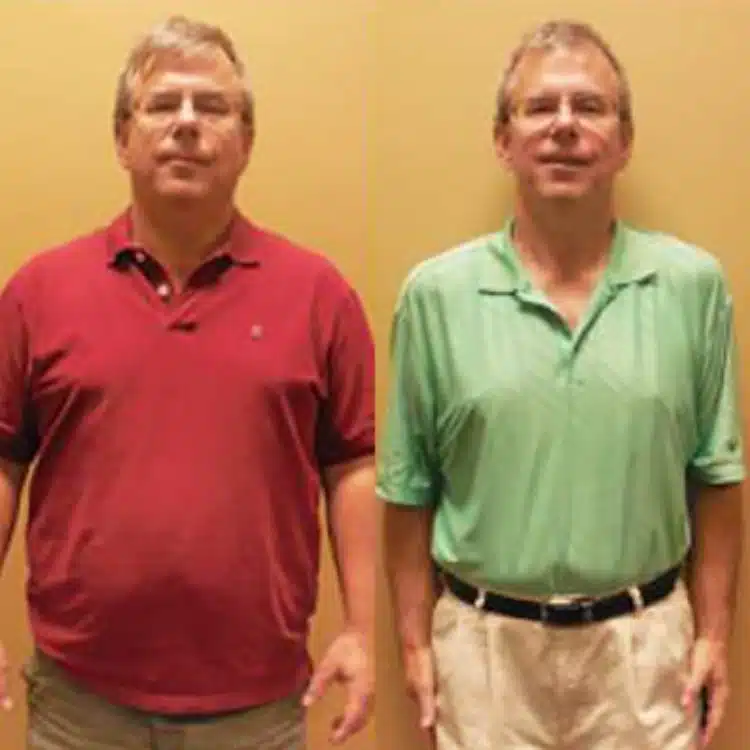
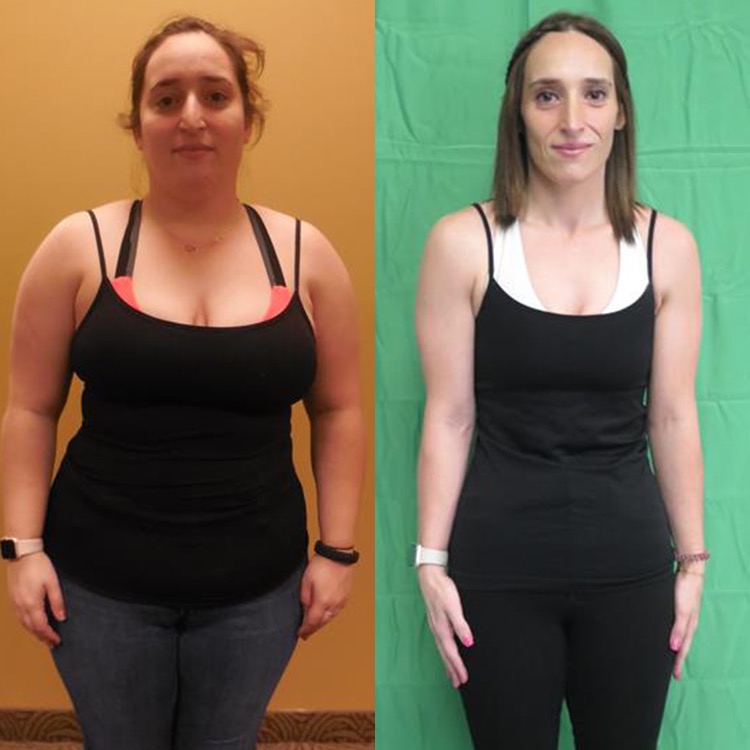
Recent clinical developments have introduced the Wegovy pill as a non-invasive option for those...
Sleep and Disease

Menopause and Weight Gain: Why It Happens and What You Can Do About It
You’re Not Imagining It—Menopause Makes Weight Loss Harder Many women notice that once menopause...
Why does fat mass loss not always result in overall weight loss
Fat Mass Loss And Overall, Weight Loss It does—but not always immediately, and not always in a...
Lose the Weight or Lose the Leg
“Lose the weight or lose the leg.” It has been over 20 years since I heard these blunt words from...
Childhood Obesity
Childhood obesity is a growing health concern worldwide, with long-term consequences for a child’s...
New Blood Pressure Guidelines: What You Need to Know
High blood pressure, also called hypertension, is one of the most common yet preventable risk...
A recent study out of the UK and France found that starting at age 50, those who slept 5 or less hours a night have a 30% increased risk of several serious, chronic diseases (see below) and by the age of 70, in those who slept five or less hours a night the risk increases to 40%.
The 12 diseases that increase with Poor Sleep include:
- Diabetes
- Cancer
- Heart Disease
- Stroke
- Heart Failure
- Chronic Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- Chronic Kidney Disease
- Liver Disease
- Depression
- Dementia
- Parkinson’s Disease
- Arthritis
In this study the researchers asked 8000 people in the UK as part of a larger study. They were asked to rate their sleep every 4-5 years and were followed for the next 25 years.
Unfortunately, if the participant slept 9 or more hours a night, those aged 60 and 70 were also at increased risk for these
chronic conditions.
In conclusion, this study reinforces the health benefits, way beyond weight, for sleep of 7-9 hours per night over a lifetime.
There were several limitations to this study.
- 2/3 were male
- 90% were white
- The data was collected via self-reports and therefore may be affected by reporting bias.
- This group also seemed to be healthier than the general population.